Explore
expand_moreIntegrating training in service
Introduction
The AI developer needs to implement 3 methods for daemon training.proto. There will be no cost borne by the consumer in calling these methods, pricing will apply when you actually call the training methods defined. AI consumer will call all these methods:
rpc create_model(CreateModelRequest) returns (ModelDetailsResponse)
rpc delete_model(UpdateModelRequest) returns (ModelDetailsResponse)
rpc get_model_status(ModelDetailsRequest) returns (ModelDetailsResponse)
Daemon will implement, however the AI developer should skip implementing these:
rpc update_model_access(UpdateModelRequest) returns (ModelDetailsResponse)
rpc get_all_models(AccessibleModelsRequest) returns (AccessibleModelsResponse)
Scheme
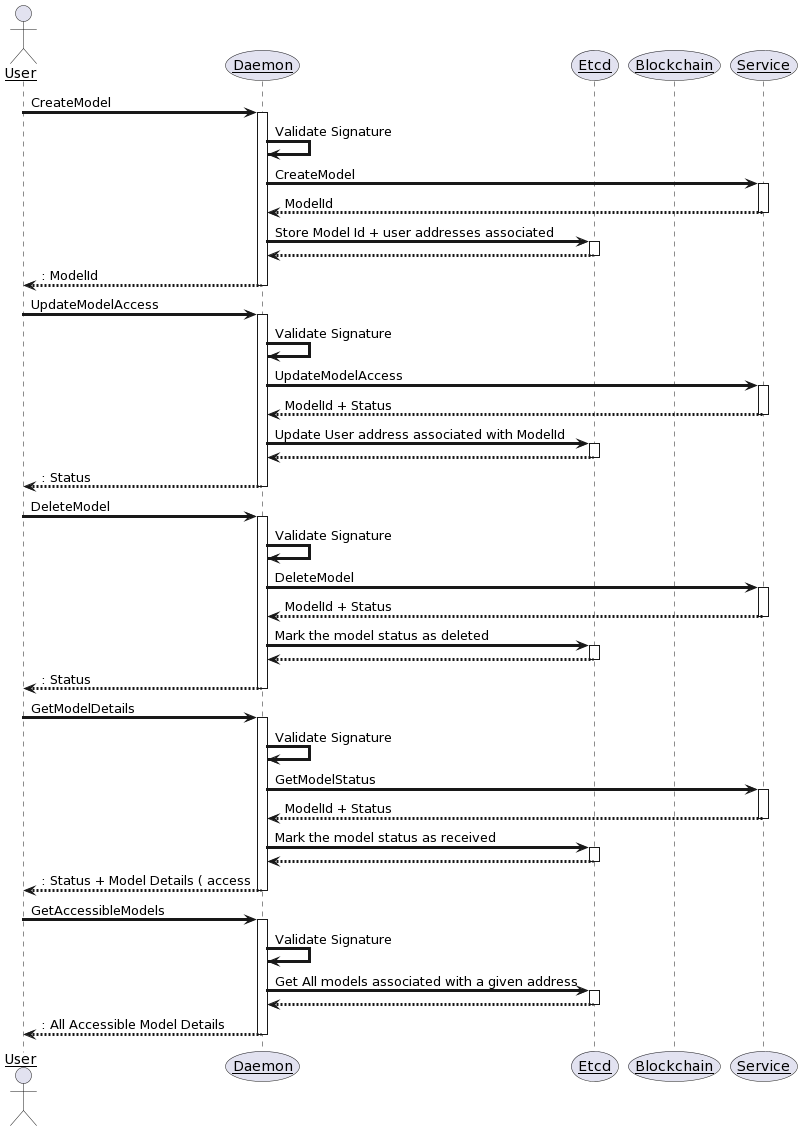
Limitations
- Only service type grpc support training;
- You can’t change training.proto file.
Step by step
-
Write your service proto file with training methods. You should mark training methods with trainingMethodIndicator from training.proto (import it):
syntax = "proto3"; import "training.proto"; package example_service; message ExampleInput { string TrainingDatasetURL = 1; } message ExampleResponse { bool IsSuccess = 1; } service ExampleTrainingService { rpc train_method(ExampleInput) returns (ExampleResponse) { option (training.my_method_option).trainingMethodIndicator = "true"; } }Also you can import and use pricing.proto (more detailed about pricing):
option (pricing.my_method_option).estimatePriceMethod = "/example_service.Calculator/dynamic_pricing_add"; -
Generate gRPC code for your programming language. For example, we will use Python.
Install grpc tools for python:
pip3 install grpc pip3 install grpcio-toolsThen generate pb files for training.proto and for your service.proto:
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --pyi_out=. --grpc_python_out=. training.proto python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --pyi_out=. --grpc_python_out=. service.proto -
Implement and write server logic for model methods. Example:
import training_pb2 import training_pb2_grpc import time import grpc from concurrent import futures import argparse _ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS = 60 * 60 * 24 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="") parser.add_argument("--host", type=str, default="0.0.0.0", help="host") parser.add_argument("--port", type=int, default=5001, help="port") args = parser.parse_args() class ExampleService(training_pb2_grpc.ModelServicer): """Provides methods that implement functionality of route guide server.""" def __init__(self): pass def create_model(self, request, context): # your logic # model_id = generate_model_ID() print("creating model...") model_id = "100" details = training_pb2.ModelDetails() details.model_id = model_id return training_pb2.ModelDetailsResponse( status=training_pb2.Status.CREATED, model_details=details ) def delete_model(self, request, context): # your logic # TODO return training_pb2.ModelDetailsResponse( status=training_pb2.Status.DELETED, model_details=request.model_details, ) def get_model_status(self, request, context): # your logic # TODO return training_pb2.ModelDetailsResponse( status=training_pb2.Status.IN_PROGRESS, model_details=request.model_details, ) def serve(): server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)) training_pb2_grpc.add_ModelServicer_to_server( ExampleService(), server ) server.add_insecure_port("{}:{}".format(args.host, args.port)) server.start() print("Server started") try: while True: time.sleep(_ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS) except KeyboardInterrupt: server.stop(0) if __name__ == "__main__": serve() -
Then implement your service proto and run service.
-
Prepare daemon config and run daemon:
model_maintenance_endpoint— this is for gRPC server endpoint for Model Maintenance like create_model, delete_model, get_model_status (example in 3 point);model_training_endpoint— this is for gRPC server endpoint for your training methods;model_training_enabled— need to be true for training.But you can use one endpoint for all configs (model_maintenance_endpoint, model_training_endpoint, passthrough_endpoint).
Notice: If in config
enable_dynamic_pricingis True and method is training (trainingMethodIndicator = “true”) request will go through model_training_endpoint instead of passthrough_endpoint. -
Test and call model methods via SDK:
from snet.sdk import SnetSDK import test_pb2_grpc # your service pb file from snet.sdk.training import training org_id = "" # TODO service_id = "" # TODO group_name = "default_groups" config = { "private_key": "", # TODO "eth_rpc_endpoint": "https://goerli.infura.io/v3", # TODO } snet_sdk = SnetSDK(config) service_client = snet_sdk.create_service_client(org_id, service_id, test_pb2_grpc.CalculatorStub, group_name) tr = training.TrainingModel() resp = tr.create_model(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_name="test_model", is_publicly_accessible=True, training_data_link="<>", description="my model") print("create_model: ", resp) model_id = resp.model_details.model_id print("new model id: ", model_id) resp = tr.get_model_status(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_id=model_id) print("get_model_status: ", resp) print("get_all_models: ", tr.get_all_models(service_client, grpc_service_name='service_name', grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add")) resp = tr.update_model_access(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_name="model_name", model_id=model_id, is_public=True, description='new description') print("delete model: ", resp) resp = tr.get_model_status(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_id=model_id) print("model status: ", resp) print("from model status: ", resp.model_details.model_id) resp = tr.delete_model(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_id=resp.model_details.model_id) print("delete model: ", resp) resp = tr.get_model_status(service_client, grpc_method_name="/example_service.Calculator/train_add", model_id=resp.model_details.model_id) print("model status: ", resp) print("from model status: ", resp.model_details.model_id)
Last modified on : 15-Oct-24